Clustering Students Based on Virtual Learning Engagement, Digital Skills, and E-learning Infrastructure: Applications of K-means, DBSCAN, Hierarchical, and Affinity Propagation Clustering
Keywords:
Clustering, Digital skill, E-learning, Students, Virtual learning engagementAbstract
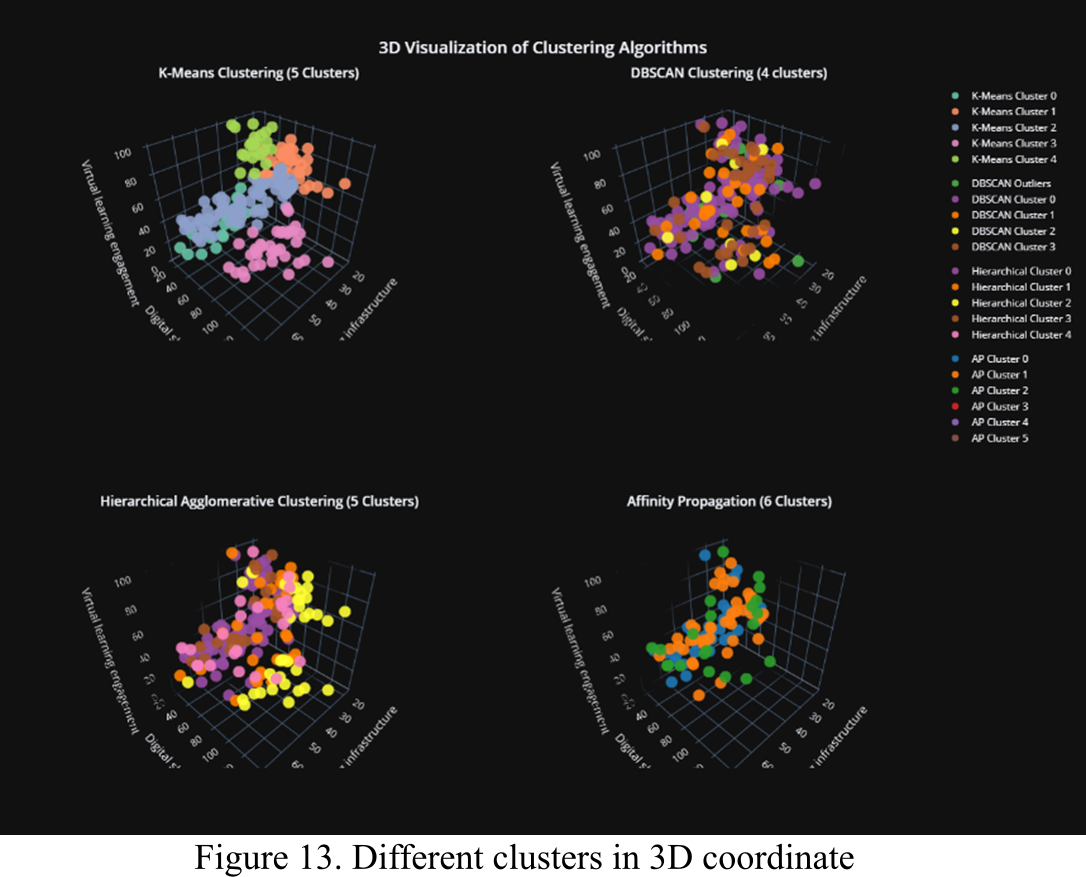
Clustering algorithms allow schools and teachers to provide students with more tailored education services. Educators are able to determine the relevant educational material to send, choose the ideal education channels for the target students, uncover new and valuable insights, and launch new instruction techniques by acquiring a better knowledge of learner characteristics. This research segmented the data for 200 students of 6 different high schools using K-means, DBSCAN, Hierarchical, and Affinity Propagation clustering algorithms. The students’ segments were determined based on their Virtual Learning Engagement, Digital Skills, and E-learning Infrastructure, which are presumably the most important characteristics to use when establishing the segments of the students attending virtual classes. This study highlights and recommend that different machine learning approaches should be implemented in order to develop segmented and personalized instruction strategies and class policies in order to enhance the effectiveness of the online classes and the level of student success.