The Adoption Of Next Generation Computing Architectures: A Meta Learning On The Adoption Of Fog, Mobile Edge, Serverless, And SoftwareDefined Computing
Keywords:
Adoption, Fog, Mobile Edge, Serverless, Software-Defined Computing, Meta LearningAbstract
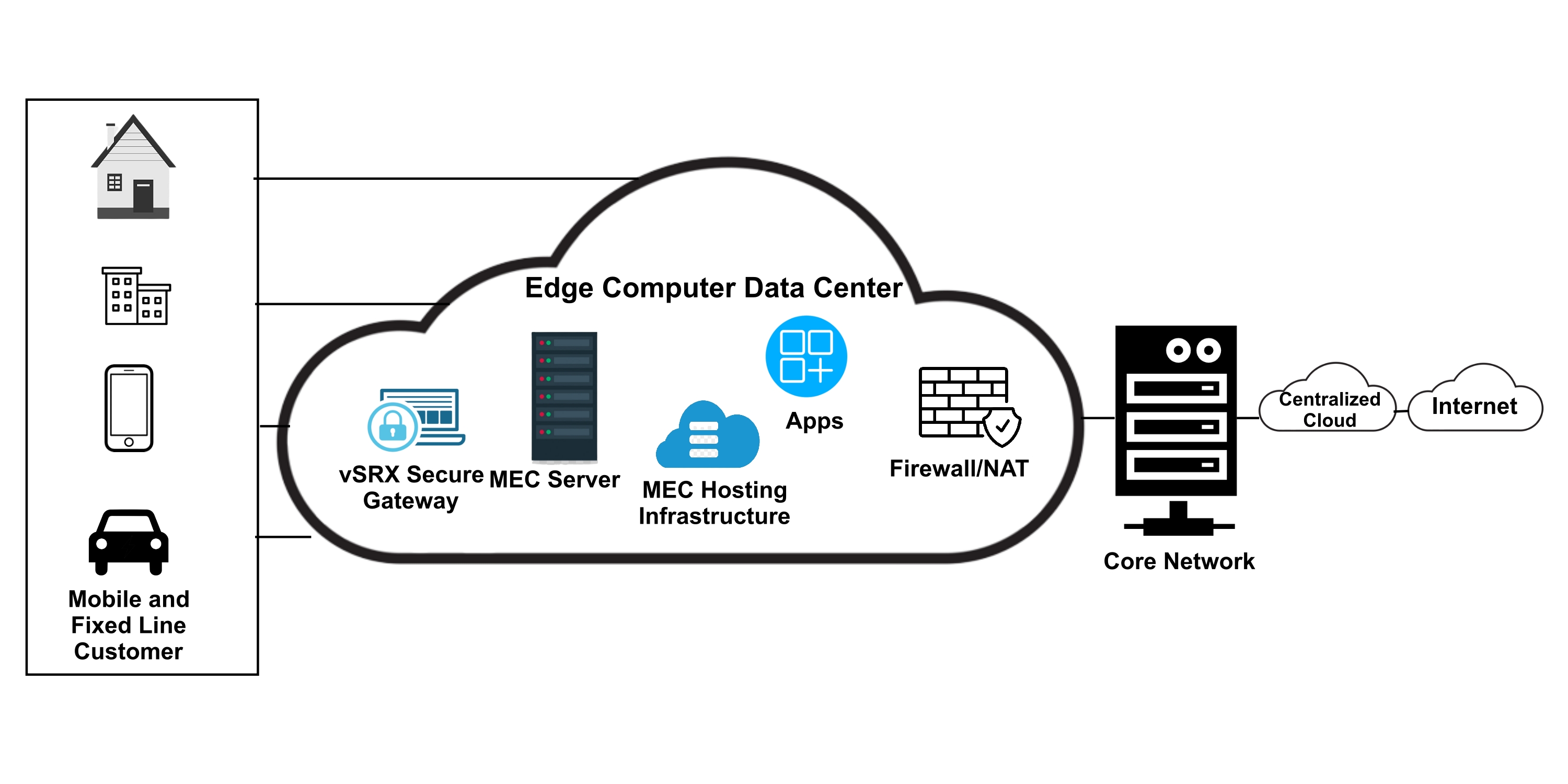
There have been several shifts in the cloud computing during the last decade. The next generation of cloud computing builds on the strengths of the current model while expanding its applicability. There will be far-reaching effects from the evolving cloud infrastructure and new computing architecture. They will be critical in facilitating the Internet-of-Things paradigm by enhancing connection between humans and IoT devices. The first purpose of this research is to review and discuss the next generation computing architectures, such as, Fog, Mobile Edge, Serverless, And Software-Defined Computing. Organizations have turned to cloud adoption as a way to increase the scalability of their Internet-based database capabilities with little outlay of resources. Cloud adoption is a deliberate decision made by businesses to reduce costs, mitigate risk, and achieve expansion of data base abilities. Depending on the amount of adoption, an organization may have varying degrees of cloud adoption. The second purpose of this is to investigate the adoption strategies of next generation cloud computing. We applied two meta learning algorithms, namely, Ensemble Voting voting and Stacking classifiers. Our results shows that most organizations with low levels of IT competence and high levels of perceived challenges are not planning to use the next generation cloud computing in the near future. Most organizations with a modest view of risk and IT competence are undecided about whether or not to adopt. Even organizations that have access to cutting-edge technology and a low level of concern about the potential challenges have mixed feelings about next generation cloud computing. Results from both classifier algorithms are almost comparable, validating the empirical findings.