Relationship between Racial Bias Exposure, Financial Literacy, and Entrepreneurial Intention: An Empirical Investigation
Keywords:
Discrimination, Entrepreneurial, Financial Literacy, Intention, Implicit Bias, Microaggressions, Stereotyping, Structural InequalityAbstract
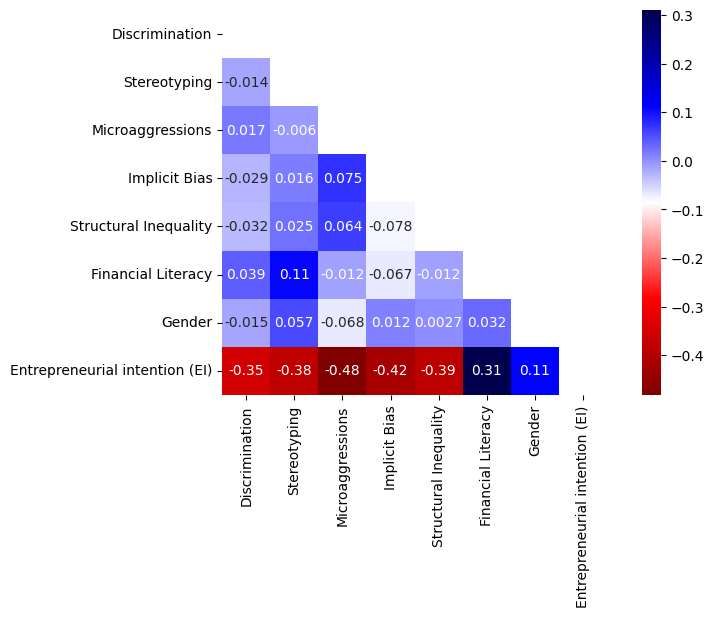
Understanding the impact of racial bias exposure on entrepreneurial intention is essential in creating a more inclusive and diverse entrepreneurial ecosystem. By studying this relationship, we can identify the underlying factors that hinder underrepresented groups from pursuing entrepreneurship and take steps to mitigate their negative effects. Using a dataset of 408 individuals from diverse ethnic groups, this study used four popular classification algorithms, including K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Support Vector Machines (SVM), Logistic Regression, and Random Forest, to analyze a diverse sample population. The results indicate that financial literacy and racial biases play significant roles in shaping entrepreneurial intention. Among the four classifiers, KNN and Random Forest performed best in identifying the most salient predictors of entrepreneurial intention. The study used 4 racial bias exposure metrics, namely, Discrimination, Stereotyping, Microaggressions, Implicit Bias, and Structural Inequality. The other two variables are Financial Literacy, and Gender. The findings show that discrimination and stereotyping have more direct and significant impacts on entrepreneurial intention than other metrics. Discrimination, which measures experiences of unfair treatment based on race, can limit an individual's access to resources, networks, and opportunities necessary for starting and growing a business. Stereotyping which measures the extent to which an individual is judged or perceived as less competent because of their race, can also impact an individual's confidence and motivation to pursue entrepreneurial goals. Stereotyping can also affect how an individual is perceived by potential investors, customers, and partners, potentially limiting their ability to attract and retain key stakeholders. The findings of this study also shows that Implicit Bias and Structural Inequality have less direct impact on entrepreneurial intention than the other metrics. While these biases can still influence behavior, they may be less directly linked to an individual's intention to start a business than more overt experiences of discrimination, stereotyping, or microaggressions. Similarly, although, Structural Inequality can have a significant impact on an individual's overall opportunities and economic mobility, it may be less directly linked to their entrepreneurial intention. The findings also show that financial literacy and gender play crucial roles in shaping an individual's mindset towards entrepreneurship, with higher levels of financial literacy and more equitable gender representation resulting in increased entrepreneurial intention. The findings of this study shed light on the importance of addressing racial biases in the entrepreneurial ecosystem and provide valuable insights for policymakers and practitioners seeking to foster inclusive and equitable entrepreneurial environments.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
CC Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0



